Satellites in orbit are essential to the day-to-day operation of the planet, but they are also the most vulnerable, and not due to human activity. Rather, it is the Sun.
As a result of increased solar activity and several geomagnetic disturbances, the Earth’s atmosphere is heating up. According to a report on spaceweather.com, solar geomagnetic storms have injected several terawatts of energy into Earth’s upper atmosphere, causing the temperature to rise.
A geomagnetic storm is a disruption in the Earth’s magnetic field brought on by the entrance of charged particles from a CME. When these particles interact with the Earth’s magnetic field, they can cause a variety of electromagnetic and electrical disturbances. CMEs, or Coronal Mass Ejections, are immense explosions of plasma and magnetic fields ejected from the Sun’s corona.
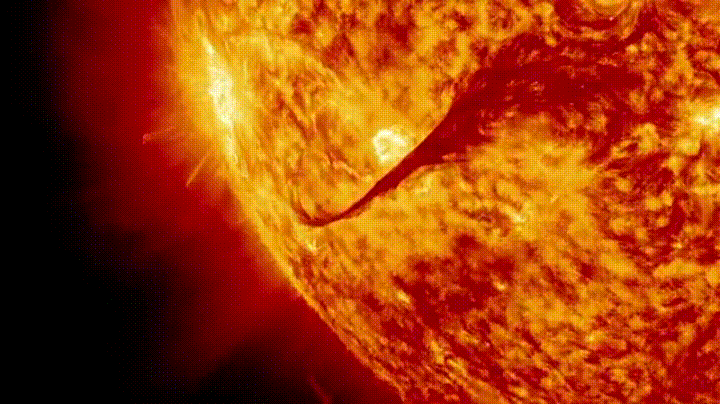
As a CME travels through space, it interacts with the solar wind and the magnetic fields of other planets. As the CME approaches Earth, it can disrupt our planet’s magnetic field, causing a geomagnetic storm.
NASA’s Martin Mlynczak indicated that increased radiation does not affect climate.
“Right now, we’re seeing some of the highest readings in the mission’s 21.5-year history,” he states. Martin has been monitoring thermosphere infrared emissions using the Saber instrument aboard NASA’s Time satellite.
The impact of a CME on Earth depends on a number of factors, including the CME’s speed and trajectory, as well as the magnetic fields’ intensity and orientation. If the CME is directed toward Earth and its magnetic fields are aligned with those of Earth, the impact could be more severe.
In the last few months, as the Sun’s activity has increased, recurrent geomagnetic storms have repeatedly struck Earth. The solar cycle is a natural occurrence caused by the magnetic field of the Sun.
The solar cycle consists of two distinct phases: the solar maximum and the solar minimum, and the Sun is presently approaching the solar maximum, which has resulted in the development of more sunspots on its surface and an increase in ejections.
